Safe Mode in Windows 10 is a diagnostic mode that starts your computer with a minimal set of drivers and services. It’s an invaluable tool for troubleshooting issues that software might cause or drivers interfering with the normal operation of Windows. This guide provides clear instructions on how to enter Safe Mode in Windows 10 and tips for making the most out of it.
What is Safe Mode?
Safe Mode is a basic state of your operating system, allowing you to run diagnostic checks. In Safe Mode, Windows operates with limited files and drivers but enough to function. This mode is particularly useful for solving issues related to software conflicts, drivers, and malware removal.
How to Enter Safe Mode in Windows 10
You can enter Safe Mode in several ways, depending on your situation.
- From Settings:
- Click on the Start menu, select the Settings icon, and then choose “Update & Security.”
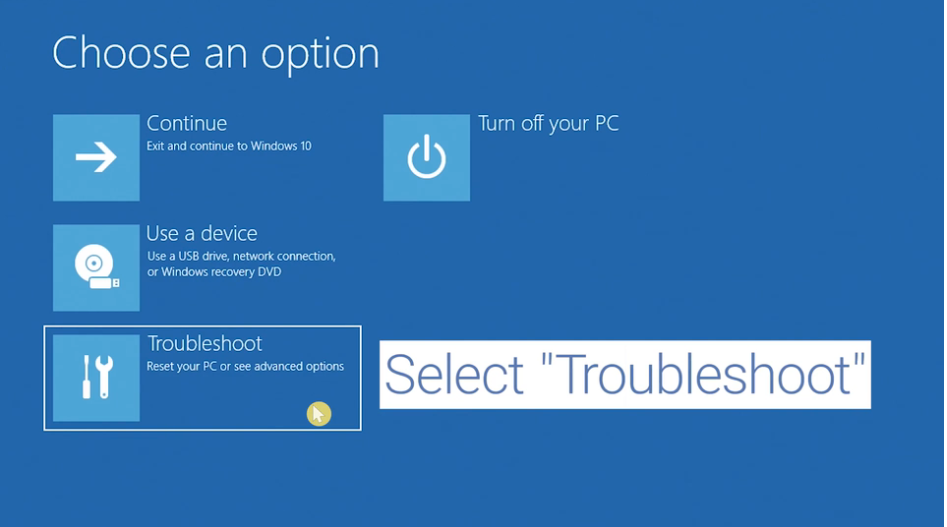
- Select “Recovery” from the left pane.
- Under “Advanced startup,” click “Restart now.”
- After your PC restarts, go to “Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings,” then click “Restart.”
- Once your PC restarts again, press 4 or F4 to start in Safe Mode. (Use 5 or F5 for Safe Mode with Networking.)
- From the Sign-in Screen: If you can’t start Windows normally, you can access Safe Mode from the sign-in screen:
- Restart your PC. At the sign-in screen, hold down the Shift key while you select Power > Restart.
- After your PC restarts, follow steps 4 and 5 from the above method.
- Using a Recovery Drive or Installation Media: If you’ve prepared a recovery drive or have installation media, you can use it to boot into Safe Mode:
- Boot from the recovery drive or installation media.
- Choose your language preferences, and click “Next.”
- Select “Repair your computer.”
- Follow steps 4 and 5 from the first method mentioned.
Tips for Using Safe Mode
- Troubleshoot Software Issues: Safe Mode is perfect for uninstalling problematic software that might not be removable in normal mode.
- Scan for Malware: Run your antivirus software in Safe Mode to remove malware more effectively.
- Update Drivers: If a recent driver update is causing issues, use Safe Mode to roll back or update drivers.
Exiting Safe Mode
To exit Safe Mode, simply restart your computer. Windows 10 will boot into its normal mode unless Safe Mode was set to start on boot through System Configuration (msconfig).
Conclusion
Safe Mode is a powerful tool for troubleshooting and fixing problems on your Windows 10 computer. By starting your PC with a minimal set of drivers and services, you can isolate the cause of many issues and resolve them. Whether you’re dealing with software conflicts, driver issues, or malware, Safe Mode is an essential step in the diagnostic process.
